Ancient Malaysian Civilization
Prehistoric Malaysia
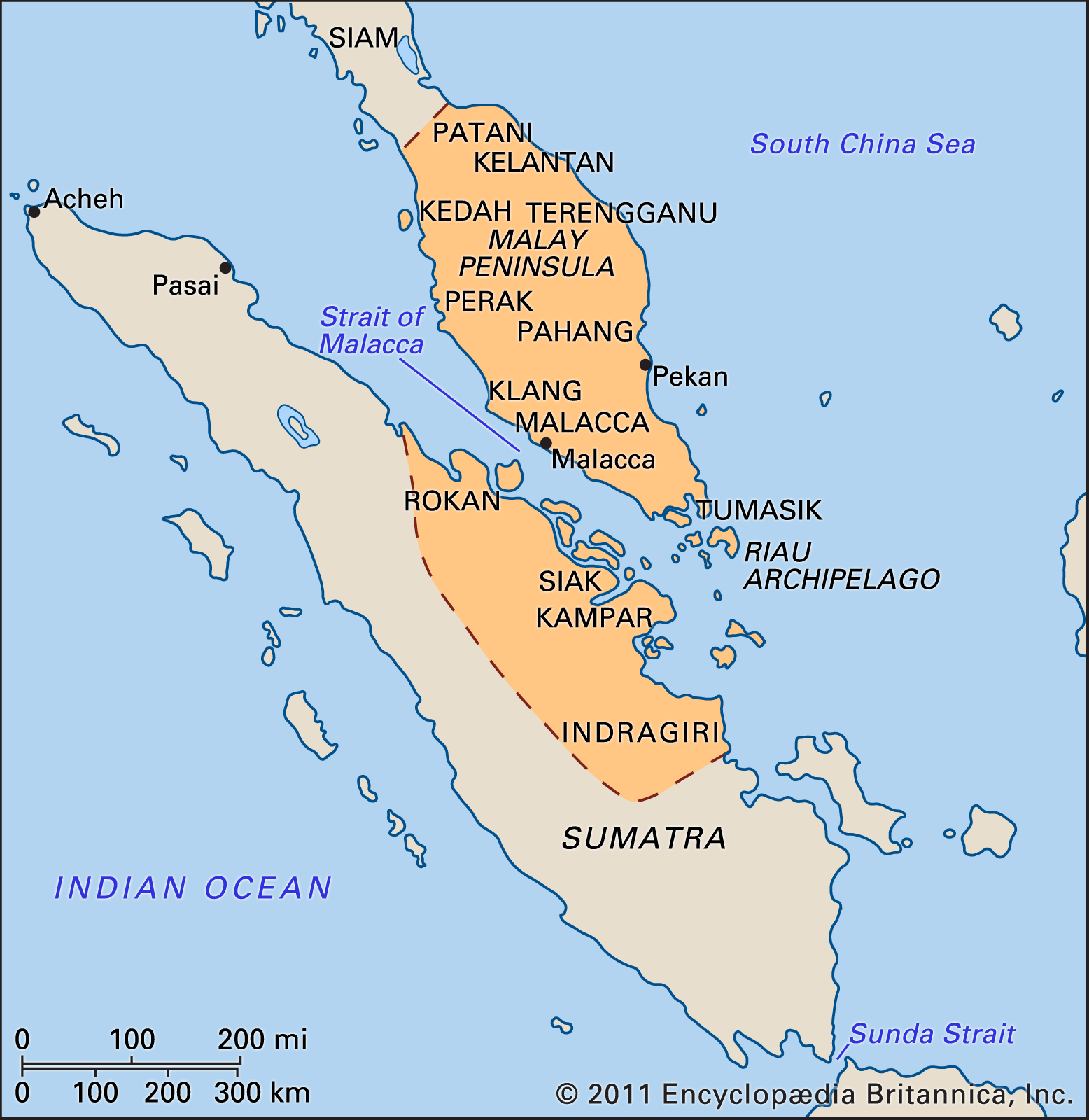
The roots of Malaysian civilization can be traced back to its prehistoric period, which reveals a rich tapestry of human activity. Archaeological findings, such as cave paintings and tools, indicate that early inhabitants engaged in hunting, gathering, and rudimentary farming.
Key highlights include:
- Tools and Artifacts: Stone tools found in locations such as Gua Niah.
- Cave Paintings: Illustrations of early human life and fauna in caves across Borneo and Peninsular Malaysia.
Early Kingdoms in Malaysia
Transitioning from prehistoric societies, Malaysia saw the emergence of early kingdoms around the 4th century, marking a significant turning point in its history.
These kingdoms, such as Langkasuka and Srivijaya, were notable for their trade and culture. As someone fascinated by history, it’s captivating to observe how these early polities influenced regional trade networks.
Features of these kingdoms included:
- Maritime Trade: Strategic locations enabled them to thrive in commerce.
- Cultural Exchange: Interactions with India and China led to the spread of Hinduism and Buddhism.
Overall, the ancient Malaysian civilization laid the groundwork for the rich cultural and political development that followed.
Colonial Era
Malacca Sultanate
Following the age of early kingdoms, the Malacca Sultanate emerged as a significant power in the 15th century. Founded by Parameswara, this sultanate became a thriving center for trade and culture, attracting merchants from around the world.
Notable aspects included:
- Strategic Location: Situated on the Strait of Malacca, it served as a crucial trade route.
- Cultural Flourishing: The blending of local customs with Islamic influences enriched the region’s heritage.
Portuguese and Dutch Colonization
However, the colonial era took a dramatic turn when the Portuguese seized Malacca in 1511, signaling the beginning of foreign dominance. They fortified their position, but soon after, the Dutch took control in the 17th century, seeking to monopolize spice trade.
The effects were profound:
- Conflict Over Trade: Numerous battles ensued for control of the lucrative trade routes.
- Cultural Imprints: Both colonizers left lasting influences on Malaysian architecture and governance.
British Rule in Malaysia
The 19th century marked a new chapter with the advent of British colonial rule. Their presence, initially solidified through the establishment of trading posts, expanded over time to encompass the Malay Peninsula.
Highlights of this period included:
- Economic Transformation: The British introduced rubber and tin, reshaping Malaysia’s economy.
- Infrastructure Development: Railways and ports were developed, creating modern transport systems.
Together, these colonial influences played a critical role in shaping Malaysia, setting the stage for its future journey towards independence.
Independence and Modern Malaysia
Japanese Occupation
The tumultuous period of World War II brought about the Japanese occupation of Malaysia from 1941 to 1945, which significantly impacted the nation’s socio-political landscape.
During this time:
- Harsh Regime: The Japanese implemented strict control, leading to food shortages and oppression.
- National Awakening: Despite the hardship, this period sparked a growing sense of nationalism among the locals.
Road to Independence
As conditions changed post-war, the desire for independence gained momentum. The British, weakened by the war, faced increasing pressure from local leaders to grant self-governance.
Key events on this journey included:
- Formation of Political Parties: Groups like the United Malays National Organization (UMNO) emerged, advocating for rights and independence.
- Negotiations: The establishment of the Malay Union and subsequent negotiations led to significant political discussions.
Malaysia as a Developing Nation
Finally, in 1957, Malaysia achieved independence, marking a pivotal moment. The nation began its journey as a developing country, focusing on unity and progress.
Highlights of contemporary Malaysia include:
- Economic Growth: Rapid industrialization and diversification of the economy, prominently featuring sectors like manufacturing and tourism.
- Cultural Cohesion: The government’s efforts in promoting multiculturalism have become a defining characteristic, fostering national identity.
Together, these experiences shaped Malaysia’s path toward becoming a dynamic, modern nation in a globalized world.
Cultural Diversity in Malaysia
Malay Culture
Malaysia’s vibrant tapestry is significantly enriched by its Malay culture, which forms the foundation of the nation. Characterized by traditional customs, art, and cuisine, Malay culture is a beautiful blend of ancient traditions and Islamic influences.
Key features include:
- Batik and Songket: Intricate textiles that showcase remarkable craftsmanship.
- Cuisine: Delightful dishes such as Nasi Lemak and Rendang that reflect local flavors and hospitality.
Chinese Influence
The Chinese community makes up a significant part of Malaysia’s demographic, and their cultural impact is profound. With their rich history and traditions, the Chinese have contributed substantially to Malaysian society.
Notable contributions include:
- Festivals: Celebrations like Chinese New Year infuse vibrancy and joy into the national calendar.
- Cuisine: Chinese food, from Dim Sum to Char Kway Teow, is beloved by all Malaysians.
Indian Community
The Indian community adds yet another layer to Malaysia’s diversity. Their presence is marked by colorful festivals, music, and culinary traditions.
Key highlights include:
- Diwali Celebrations: An exuberant festival of lights that brings communities together.
- Cuisine: Indian dishes like Roti Canai and Satay are not only staples but also showcase the culinary fusion found in Malaysia.
Together, these cultures create a harmonious blend that makes Malaysia unique, allowing for a vibrant exchange of traditions and lifestyles.
Economic Development
Industrialization in Malaysia
As Malaysia embraced independence, one of the pivotal shifts witnessed was rapid industrialization. This transformative phase began in the late 20th century, shifting the economy from agriculture to manufacturing.
Key developments included:
- Establishment of Factories: A surge in manufacturing plants created jobs and enhanced the economy.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Attracting international investors helped bolster industrial capabilities.
Major Economic Sectors
Today, Malaysia’s economy thrives on several key sectors, each contributing uniquely to its growth.
Notable sectors include:
- Manufacturing: Electronics and electrical goods account for a significant portion of exports.
- Agriculture: Palm oil remains a major export, showcasing the nation’s agricultural strength.
- Services: Tourism and finance have gained momentum, reflecting Malaysia’s diverse economic landscape.
Malaysia’s Global Trade Role
With its robust industrial and economic framework, Malaysia has positioned itself as a vital player in global trade. Its strategic location along major shipping routes enhances its export capabilities.
Highlights of Malaysia’s trade role include:
- Trade Agreements: Participation in agreements like ASEAN fosters economic collaboration.
- Diverse Export Markets: Malaysia reaches customers worldwide, from electronics to agricultural products.
In summary, Malaysia’s economic development journey underscores its transformation into a vital regional powerhouse, marked by diversification and globalization.
Political Landscape
Government Structure
As Malaysia’s economy flourished, so did its political framework. The nation operates under a federal constitutional monarchy, where the Yang di-Pertuan Agong serves as the monarch, complemented by a parliamentary system.
Key features include:
- Bicameral Legislature: The Parliament consists of the House of Representatives and the Senate, ensuring representation.
- State Governments: Each state maintains its own government with considerable autonomy, fostering localized governance.
Political Parties in Malaysia
Malaysia’s political scene is vibrant, with numerous parties vying for influence and power. The two primary coalitions, Barisan Nasional and Pakatan Harapan, represent a diverse spectrum of ideologies and ethnicities.
Highlights of political parties include:
- Barisan Nasional: Traditionally dominant, emphasizing national unity and economic growth.
- Pakatan Harapan: A relatively newer coalition advocating for reforms and transparency.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its advancements, Malaysia faces political challenges that test its stability. Issues like corruption and ethnic divides complicate the political landscape.
Key challenges include:
- Navigating Ethnic Relations: Balancing the interests of Malaysia’s diverse communities remains crucial.
- Political Stability: Ensuring a stable government is vital for ongoing economic progress.
Looking ahead, Malaysia’s political landscape will need to adapt and innovate to meet these challenges, paving the way for a more united and prosperous future.
Contemporary Issues
Social Issues
As Malaysia continues to develop, it faces several social issues that challenge its progress. Inequality and access to education remain significant concerns.
Key highlights include:
- Economic Disparities: Certain regions experience stark differences in wealth and opportunities.
- Youth Unemployment: A growing population of young graduates is struggling to find employment that matches their skills.
Environmental Concerns
Alongside social challenges, environmental issues have emerged as critical topics. Deforestation and pollution pose serious threats to Malaysia’s rich biodiversity.
Notable concerns include:
- Deforestation: Rapid industrialization often results in habitat loss for many species.
- Pollution: Urbanization has led to air and water quality issues, impacting public health.
Malaysia’s Role in International Relations
In the realm of international relations, Malaysia strives to position itself as a key player, balancing relationships with major powers while promoting regional stability.
Key aspects include:
- ASEAN Membership: Active participation in ASEAN fosters economic and cultural cooperation in Southeast Asia.
- Global Trade Agreements: Malaysia leverages trade partnerships to enhance its economic standing on the world stage.
Thus, addressing these contemporary issues is paramount for Malaysia’s growth and its image in the global arena.